Advertisement
If you're new to the world of big data and distributed computing, there's a good chance you've stumbled upon YARN — and perhaps shrugged it off as just another acronym. But here’s what makes it worth your attention: YARN plays a key role in handling the chaos that comes with running many jobs across many machines. Without it, things can slow down, overlap, or even fail entirely.
Understanding YARN doesn’t require a computer science degree. What helps is thinking of it as the one keeping everything fair, smooth, and on schedule. Whether you're experimenting locally or working with a growing cluster, knowing how YARN functions can make the process clearer — and your work more efficient.
YARN stands for Yet Another Resource Negotiator. The name is quirky, but the function is practical. Introduced with Hadoop 2.0, it was designed to solve a growing problem: the original version of Hadoop put too much responsibility on a single framework, MapReduce, which managed both the data crunching and the resource tracking. That setup worked when things were small. But as data and demands grew, the cracks began to show.
YARN stepped in to separate concerns. Instead of having your data processing tool also manage who gets what resources and when, YARN took over that second job. It doesn’t process the data itself — it simply decides which tasks go where and ensures they have the memory and CPU they need to run. That leaves tools like Spark, Hive, and MapReduce free to focus on actual computation.
Let's make this less abstract. Think of YARN as a team, where each part has its job. If you imagine a company working on multiple projects at once, you'll get a sense of how these pieces operate.
The ResourceManager handles the big picture. It knows what tasks need to be run, what resources are available, and how to divide them up. It doesn’t touch the data, but it makes the high-level decisions about where work should happen.
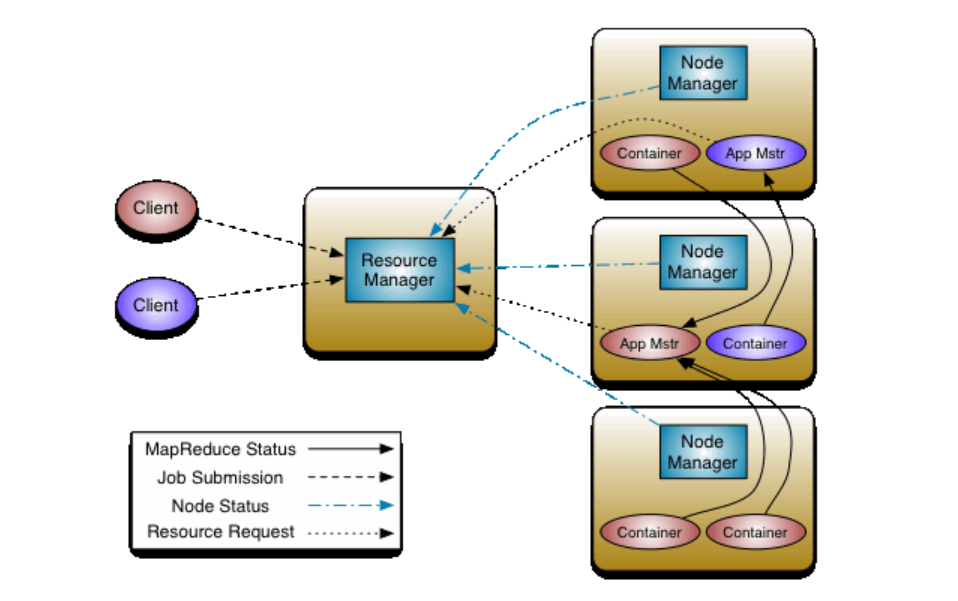
Each machine in the cluster runs a NodeManager. This component reports back to the ResourceManager with updates on resource usage and task status. It’s like a local supervisor — aware of what’s going on in its own space and responsible for launching tasks when told.
Every job you run creates its own ApplicationMaster. It speaks with the ResourceManager to request resources, then coordinates the actual work within the cluster. Once the job is done, the ApplicationMaster wraps up and exits.
Each task runs inside a container. A container is just an isolated environment with the memory and CPU it needs to do its job. These aren't physical — they’re logical allocations of resources, assigned by YARN when a task starts.
One of the main reasons YARN is used so widely is its ability to manage clusters of hundreds or even thousands of machines without getting overwhelmed. It’s structured in a way that avoids bottlenecks and keeps everything organized, even under pressure.
YARN doesn't hand out all resources at once. Instead, it looks at what's available, what’s currently in use, and what just got freed up. Based on this, it makes real-time decisions. If a job wraps up early, its container space can be reassigned quickly — no wasted cycles, no idle machines.
If a node crashes, the system doesn’t grind to a halt. The NodeManager stops sending updates, the ResourceManager notices, and work is shifted elsewhere. This automatic rebalancing means no single point of failure becomes a full-blown disaster.
In environments where different teams submit jobs at the same time, YARN prevents resource conflicts. Whether you’re running batch jobs, interactive queries, or streaming applications, it ensures that no single job gets too greedy. Everyone gets a reasonable share, and high-priority work can be scheduled accordingly.
Now that you have a grasp on what YARN does, let’s look at how to actually use it. You don’t need a full data center to get started — just a computer and some time.
YARN is part of the Hadoop ecosystem. To start, install Hadoop on your machine. Begin in pseudo-distributed mode, which lets you run everything locally but still see how the pieces interact.
Once set, format the NameNode and start Hadoop's services.
Once Hadoop is configured, launching YARN is simple.
bash
CopyEdit
start-yarn.sh
This command starts the ResourceManager and NodeManager. Open your browser and go to http://localhost:8088 to confirm it's running — this page will show the current status of the system and give you a look at how resources are being used.
To see how YARN actually handles workload, use one of the built-in examples that Hadoop provides. This helps you observe resource coordination in real-time.
bash
CopyEdit
hadoop jar share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-*.jar wordcount input output
This classic word count job processes a text file and outputs the frequency of each word. YARN coordinates everything under the hood: resource negotiation, container allocation, and status tracking.
Once the job is submitted, check the ResourceManager interface. You’ll see task progress, memory use, and whether any containers failed. This kind of live insight becomes especially helpful later, when troubleshooting more complex jobs or trying to fine-tune performance.
YARN doesn’t demand that you be an expert in distributed systems. What it offers is a way to bring order to the natural messiness of large-scale computing. It separates the task of doing the work from the task of managing resources — a small shift with big results.
Whether you’re learning on a laptop or preparing for enterprise-scale operations, the structure YARN provides will help your applications run better. You’ll avoid unnecessary slowdowns, make better use of available hardware, and understand more about how resources behave in real time.
Advertisement
How fine-tuning CLIP with satellite data improves its performance in interpreting remote sensing images and captions for tasks like land use mapping and disaster monitoring
Curious about how to start your first machine learning project? This beginner-friendly guide walks you through choosing a topic, preparing data, selecting a model, and testing your results in plain language

How the Annotated Diffusion Model transforms the image generation process with transparency and precision. Learn how this AI technique reveals each step of creation in clear, annotated detail

How does HDFS handle terabytes of data without breaking a sweat? Learn how this powerful distributed file system stores, retrieves, and safeguards your data across multiple machines

Thinking of moving to the cloud? Discover seven clear reasons why businesses are choosing Google Cloud Platform—from seamless scaling and strong security to smarter collaboration and cost control

Confused about the difference between a data lake and a data warehouse? Discover how they compare, where each shines, and how to choose the right one for your team

How to convert transformers to ONNX with Hugging Face Optimum to speed up inference, reduce memory usage, and make your models easier to deploy across platforms

Confused about MLOps? Learn how MLflow makes machine learning deployment, versioning, and collaboration easier with real-world workflows for tracking, packaging, and serving models

New to YARN? Learn how YARN manages resources in Hadoop clusters, improves performance, and keeps big data jobs running smoothly—even on a local setup. Ideal for beginners and data engineers

Is your team using AI tools you don’t know about? Shadow AI is growing inside companies fast—learn how to manage it without stifling innovation or exposing your data

Explore how Google Cloud Platform (GCP) powers scalable, efficient, and secure applications in 2025. Learn why developers choose GCP for data analytics, app development, and cloud infrastructure

Learn the full process of deploying ViT on Vertex AI for scalable and efficient image classification. Discover how to prepare, containerize, and serve Vision Transformer models in production